6 Using the XSLT Processor for Java
This chapter contains these topics:
Introduction to the XSLT Processor
This section contains the following topics:
Prerequisites
XSLT is an XML-based language that you can use to transform one XML document into another text document. For example, you can use XSLT to accept an XML data document as input, perform arithmetic calculations on element values in the document, and generate an XHTML document that shows the calculation results.In XSLT, XPath is used to navigate and process elements in the source node tree. XPath models an XML document as a tree made up of nodes; the types of nodes in the XPath node tree correspond to the types of nodes in a DOM tree.
This chapter assumes that you are familiar with the following W3C standards:
-
eXtensible Stylesheet Language (XSL) and eXtensible Stylesheet Language Transformation (XSLT). If you require a general introduction to XSLT, consult the XML resources listed in "Related Documents" of the preface.
Standards and Specifications
XSLT is currently available in two versions: a working draft for XSLT 2.0 and the XSLT 1.0 Recommendation. You can find the specifications at the following URLs:
XPath, which is the navigational language used by XSLT and other XML languages, is available in two versions: a working draft for XPath 2.0 and the XPath 1.0 Recommendation. You can find the specifications for the two XPath versions at the following URLs:
Oracle XDK XSLT processor implements both the XSLT and XPath 1.0 standards as well as the current working drafts of the XSLT and XPath 2.0 standards. The XDK XSLT processor supports the XPath 2.0 functions and operators. You can find the specification at the following URL:
http://www.w3.org/TR/xpath-functions/
See Also:
Chapter 31, "XDK Standards" for a summary of the standards supported by the XDKXML Transformation with XSLT 1.0 and 2.0
In Oracle Database 10g, the XDK provides several useful features not included in XSLT 1.0. To use XSLT 2.0, set the version attribute in your stylesheet as follows:
<? xml-stylesheet version="2.0" ... ?>
Some of the most useful XSLT 2.0 features are the following:
-
User-defined functions
You can use the
<xsl:function>declaration to define functions. This element must have onenameattribute to define the function name. The value of thenameattribute is aQName. The content of the<xsl:function>element is zero or morexsl:paramelements that specify the formal arguments of the function, followed by a sequence constructor that defines the value returned by the function.Note that
QNamecan have a null namespace, but user-defined functions must have a non-null namespace. That is, ifabcis defined as a namespace, thenaddis not a legal user-defined function, butabc:addis. -
Grouping
You can use the
<xsl:for-each-group>element,current-group()function, andcurrent-grouping-key()function to group items. -
Multiple result documents
You can use the
<xsl:result-document>element to create a result tree. The content of the<xsl:result-document>element is a sequence constructor for the children of the document node of the tree.For example, this element enables you to accept an XML document as input and break it into separate documents. You can take an XML document that describes a list of books and generate an XHTML document for each book. You can then validate each output document.
-
Temporary trees
Instead of representing the intermediate XSL transformation results and XSL variables as strings, as in XSLT 1.0, you can store them as a set of document nodes. The document nodes, which you can construct with the
<xsl:variable>,<xsl:param>, and<xsl:with-param>elements, are called temporary trees. -
Character mapping
In XSLT 1.0, you had to use the
disable-output-escapingattribute of the<xsl:text>and<xsl:value-of>elements to specify character escaping. In XSLT 2.0, you can declare mapping characters with an<xsl:character-map>element as a top level stylesheet element. You can use this element to generate files with reserved or invalid XML characters in the XSLT outputs, such as<,>, and&.
See Also:
http://www.w3.org/TR/xslt20 for explanation and examples of XSLT 2.0 featuresUsing the XSLT Processor for Java: Overview
The Oracle XDK XSLT processor is a software program that transforms an XML document into another text-based format. For example, the processor can transform XML into XML, HTML, XHTML, or text. You can invoke the processor programmatically by using the APIs or run it from the command line. The XSLT processor can perform the following tasks:
-
Reads one or more XSLT stylesheets. The processor can apply multiple stylesheets to a single XML input document and generate different results.
-
Reads one or more input XML documents. The processor can use a single stylesheet to transform multiple XML input documents.
-
Builds output documents by applying the rules in the stylesheet to the input XML documents. The output is a DOM tree, output stream, or series of SAX events.
Whereas XSLT is a function-based language that generally requires a DOM of the input document and stylesheet to perform the transformation, the Java XDK implementation of the XSLT processor can use SAX to create a stylesheet object to perform transformations with higher efficiency and fewer resources. You can reuse this stylesheet object to transform multiple documents without reparsing the stylesheet.
Using the XSLT Processor: Basic Process
Figure 6-1 depicts the basic design of the XSLT processor for Java.
See Also:
Oracle Database XML Java API Reference to learn about theXMLParser and XSDBuilder classesFigure 6-1 Using the XSLT Processor for Java
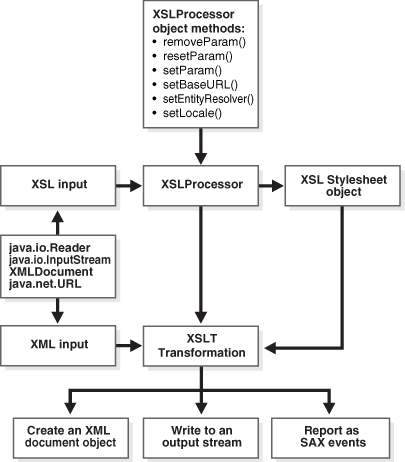
Description of "Figure 6-1 Using the XSLT Processor for Java"
Running the XSLT Processor Demo Programs
Demo programs for the XSLT processor for Java are included in $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/java/parser/xslt. Table 6-1 describes the XML files and programs that you can use to test the XSLT processor.
Table 6-1 XSLT Processor Sample Files
| File | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
A sample XML document that you can use to test ID selection and pattern matching. Its associated stylesheet is |
|
|
A sample stylesheet for use with |
|
|
A sample XML data document that you can use to perform simple arithmetic. Its associated stylesheet is |
|
|
A sample stylesheet for use with |
|
|
A sample XML data document that you can use to test for source tree numbering. The document describes the structure of a book. |
|
|
A sample stylesheet for us with |
|
|
A sample XML data document that you can use to test for |
|
|
A sample stylesheet for use with |
|
|
A sample XML data document that you can use with |
|
|
A sample stylesheet for us with |
|
|
A sample XML data document that you can use to test perform various string test and manipulations. Its associated stylesheet is |
|
|
A sample stylesheet for us with |
|
|
A stylesheet that provides the framework for an HTML page. The stylesheet is included by |
|
|
A sample XML data document that you can use to test the use of XSL variables. The document describes the structure of a book. Its associated stylesheet is |
|
|
A stylesheet for use with |
|
|
A sample application that offers a simple example of how to use the XSL processing capabilities of the Oracle XSLT processor. The program transforms an input XML document by using an input stylesheet. This program builds the result of XSL transformations as a Run this program with any XSLT stylesheet in the directory as a first argument and its associated |
|
|
A sample application that offers a simple example of how to use the XSL processing capabilities of the Oracle XSLT processor. The program transforms an input XML document by using an input stylesheet. This program outputs the result to a stream and supports |
Documentation for how to compile and run the sample programs is located in the README. The basic steps are as follows:
-
Change into the
$ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/java/parser/xsltdirectory (UNIX) or%ORACLE_HOME%\xdk\demo\java\parser\xsltdirectory (Windows). -
Make sure that your environment variables are set as described in "Setting Up the Java XDK Environment".
-
Run
make(UNIX) orMake.bat(Windows) at the command line. The make file compiles the source code and then runs theXSLSampleandXSLSample2programs for each*.xmlfile and its associated*.xslstylesheet. The program writes its output for each transformation to*.out. -
You can view the
*.outfiles to see the output for the XML transformations. You can also run the programs on the command line as follows, wherenameis replaced bymatch,math, and so forth:java XSLSample name.xsl name.xml java XSLSample2 name.xsl name.xml
For example, run the
match.xmldemos as follows:java XSLSample match.xsl match.xml java XSLSample2 match.xsl match.xml
Using the XSLT Processor Command-Line Utility
The XDK includes oraxsl, which is a command-line Java interface that can apply a stylesheet to multiple XML documents. The $ORACLE_HOME/bin/oraxsl and %ORACLE_HOME%\bin\oraxsl.bat shell scripts execute the oracle.xml.jaxb.oraxsl class. To use oraxsl ensure that your CLASSPATH is set as described in "Setting Up the Java XDK Environment".
Use the following syntax on the command line to invoke oraxsl:
oraxsl options source stylesheet result
The oraxsl utility expects a stylesheet, an XML file to transform, and an optional result file. If you do not specify a result file, then the utility sends the transformed document to standard output. If multiple XML documents need to be transformed by a stylesheet, then use the -l or -d options in conjunction with the -s and -r options. These and other options are described in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2 Command-Line Options for oraxsl
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Shows warnings. By default, warnings are turned off. |
|
|
Specifies file into which the program writes errors and warnings. |
|
|
Lists files to be processed. |
|
|
Specifies the directory that contains the files to transform. The default behavior is to process all files in the directory. If only a subset of the files in that directory, for example, one file, need to be processed, then change this behavior by setting |
|
|
Specifies extensions for the files that should be excluded. Use this option in conjunction with |
|
|
Specifies extensions for the files that should be included. Use this option in conjunction with |
|
|
Specifies the stylesheet. If you set |
|
|
Specifies the extension to use for results. If you set |
|
|
Specifies the directory in which to place results. You must set this option in conjunction with the |
|
|
Lists parameters. |
|
|
Specifies the number of threads to use for processing. Using multiple threads can provide performance improvements when processing multiple documents. |
|
|
Generates verbose output. The program prints some debugging information and can help in tracing any problems that are encountered during processing. |
|
|
Generates debugging output. By default, debug mode is disabled. Note that a GUI version of the XSLT debugger is available in Oracle JDeveloper. |
Using the XSLT Processor Command-Line Utility: Example
You can test oraxsl on the various XML files and stylesheets in $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/java/parser/xslt. Example 6-1 displays the contents of math.xml.
<?xml version="1.0"?> <doc> <n1>5</n1> <n2>2</n2> <div>-5</div> <mod>2</mod> </doc>
The XSLT stylesheet named math.xsl is shown in Example 6-2.
<?xml version="1.0"?><xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:template match="doc">
<HTML>
<H1>Test for mod.</H1>
<HR/>
<P>Should say "1": <xsl:value-of select="5 mod 2"/></P>
<P>Should say "1": <xsl:value-of select="n1 mod n2"/></P>
<P>Should say "-1": <xsl:value-of select="div mod mod"/></P>
<P><xsl:value-of select="div or ((mod)) | or"/></P>
</HTML>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet
You can run the oraxsl utility on these files to produce HTML output as shown in the following example:
oraxsl math.xml math.xsl math.htm
The output file math.htm is shown in Example 6-3.
Transforming XML
This section contains the following topics:
Performing Basic XSL Transformation
As explained in "Using the XSLT Processor for Java: Overview", the fundamental classes used by the XSLT processor are DOMParser and XSLProcessor. The XSL2Sample.java demo program provides a good illustration of how to use these classes to transform an XML document with an XSLT stylesheet.
Use the following basic steps to write Java programs that use the XSLT processor:
-
Create a DOM parser object that you can use to parse the XML data documents and XSLT stylesheets. The following code fragment from
XSL2Sample.javaillustrates how to instantiate a parser:XMLDocument xml, xsldoc, out;URL xslURL;URL xmlURL; // ... parser = new DOMParser();parser.setPreserveWhitespace(true);
Note that by default, the parser does not preserve whitespace unless a DTD is used. It is important to preserve whitespace because it enables XSLT whitespace rules to determine how whitespace is handled.
-
Parse the XSLT stylesheet with the
DOMParser.parse()method. The following code fragment fromXSL2Sample.javaillustrates how to perform the parse:xslURL = DemoUtil.createURL(args[0]); parser.parse(xslURL); xsldoc = parser.getDocument();
-
Parse the XML data document with the
DOMParser.parse()method. The following code fragment fromXSL2Sample.javaillustrates how to perform the parse:xmlURL = DemoUtil.createURL(args[1]); parser.parse(xmlURL); xml = parser.getDocument();
-
Create a new XSLT stylesheet object. You can pass objects of the following classes to the
XSLProcessor.newXSLStylesheet()method:-
java.io.Reader -
java.io.InputStream -
XMLDocument -
java.net.URL
For example,
XSL2Sample.javaillustrates how to create a stylesheet object from anXMLDocumentobject:XSLProcessor processor = new XSLProcessor(); processor.setBaseURL(xslURL); XSLStylesheet xsl = processor.newXSLStylesheet(xsldoc);
-
-
Set the XSLT processor to display any warnings. For example,
XSL2Sample.javacalls theshowWarnings()andsetErrorStream()methods as follows:processor.showWarnings(true); processor.setErrorStream(System.err);
-
Use the
XSLProcessor.processXSL()method to apply the stylesheet to the input XML data document. Table 6-3 lists some of the other availableXSLProcessormethods.Table 6-3 XSLProcessor Methods
Method Description removeParam()Removes parameters.
resetParams()Resets all parameters.
setParam()Sets parameters for the transformation.
setBaseUrl()Sets a base URL for any relative references in the stylesheet.
setEntityResolver()Sets an entity resolver for any relative references in the stylesheet.
setLocale()Sets a locale for error reporting.
The following code fragment from
XSL2Sample.javashows how to apply the stylesheet to the XML document:processor.processXSL(xsl, xml, System.out);
-
Process the transformed output. You can transform the results by creating an XML document object, writing to an output stream, or reporting SAX events.
The following code fragment from
XSL2Sample.javashows how to print the results:processor.processXSL(xsl, xml, System.out);
Obtaining DOM Results from an XSL Transformation
The XSLSample.java demo program illustrates how to generate an oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLDocumentFragment object as the result of an XSL transformation. An XMLDocumentFragment is a "lightweight" Document object that extracts a portion of an XML document tree. The XMLDocumentFragment class implements the org.w3c.dom.DocumentFragment interface.
The XSL2Sample.java program illustrates how to generate a DocumentFragment object. The basic steps for transforming XML are the same as those described in "Performing Basic XSL Transformation". The only difference is in the arguments passed to the XSLProcessor.processXSL() method. The following code fragment from XSL2Sample.java shows how to create the DOM fragment and then print it to standard output:
XMLDocumentFragment result = processor.processXSL(xsl, xml); result.print(System.out);
Table 6-4 lists some of the XMLDocumentFragment methods that you can use to manipulate the object.
Table 6-4 XMLDocumentFragment Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Gets a |
|
|
Gets the local name for this element |
|
|
Gets the namespace URI of this element |
|
|
Gets the node immediately following the current node |
|
|
Gets the name of the node |
|
|
Gets a code that represents the type of the underlying object |
|
|
Gets the parent of the current node |
|
|
Gets the node immediately preceding the current node |
|
|
Reports SAX events from a DOM Tree |
Programming with Oracle XSLT Extensions
This section contains these topics:
Overview of Oracle XSLT Extensions
The XSLT 1.0 standard defines two kinds of extensions: extension elements and extension functions. The XDK provides extension functions for XSLT processing that enable users of the XSLT processor to call any Java method from XSL expressions. Note the following guidelines when using Oracle XSLT extensions:
-
When you define an XSLT extension in a given programming language, you can only use the XSLT stylesheet with XSLT processors that can invoke this extension. Thus, only the Java version of the processor can invoke extension functions that are defined in Java.
-
Use XSLT extensions only if the built-in XSL functions cannot solve a given problem.
-
As explained in the following section, the namespace of the extension class must start with the proper URL.
The following Oracle extension functions are particularly useful:
-
<ora:output>, you can use<ora:output>as a top-level element or in an XSL template. If used as a top-level element, it is similar to the<xsl:output>extension function, except that it has an additionalnameattribute. When used as a template, it has the additional attributesuseandhref. This function is useful for creating multiple outputs from one XSL transformation. -
<ora:node-set>, which converts a result tree fragment into a node-set. This function is useful when you want to refer the existing text or intermediate text results in XSL for further transformation.
Specifying Namespaces for XSLT Extension Functions
The Oracle Java extension functions belong to the namespace that corresponds to the following URI:
http://www.oracle.com/XSL/Transform/java/
An extension function that belongs to the following namespace refers to methods in the Java classname, so that you can construct URIs in the following format:
http://www.oracle.com/XSL/Transform/java/classname
For example, you can use the following namespace to call java.lang.String methods from XSL expressions:
http://www.oracle.com/XSL/Transform/java/java.lang.String
Note:
When assigning thexsl prefix to a namespace, the correct URI is xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform". Any other URI fails to give correct output.Using Static and Non-Static Java Methods in XSLT
If the Java method is a non-static method of the class, then the first parameter is used as the instance on which the method is invoked, and the rest of the parameters are passed to the method. If the extension function is a static method, however, then all the parameters of the extension function are passed as parameters to the static function. Example 6-4 shows how to use the java.lang.Math.ceil() method in an XSLT stylesheet.
Example 6-4 Using a Static Function in an XSLT Stylesheet
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:math="http://www.oracle.com/XSL/Transform/java/java.lang.Math">
<xsl:template match="/">
<xsl:value-of select="math:ceil('12.34')"/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
For example, you can create Example 6-4 as stylesheet ceil.xsl and then apply it to any well-formed XML document. For example, run the oraxsl utility as follows:
oraxsl ceil.xsl ceil.xsl ceil.out
The output document ceil.out has the following content:
<?xml version = '1.0' encoding = 'UTF-8'?> 13
Note:
The XSL class loader only knows about statically added JARs and paths in theCLASSPATH as well as those specified by wrapper.classpath. Files added dynamically are not visible to XSLT processor.Using Constructor Extension Functions
The extension function new creates a new instance of the class and acts as the constructor. Example 6-5 creates a new String object with the value "Hello World," stores it in the XSL variable str1, and then outputs it in uppercase.
Example 6-5 Using a Constructor in an XSLT Stylesheet
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:jstring="http://www.oracle.com/XSL/Transform/java/java.lang.String">
<xsl:template match="/">
<!-- creates a new java.lang.String and stores it in the variable str1 -->
<xsl:variable name="str1" select="jstring:new('HeLlO wOrLd')"/>
<xsl:value-of select="jstring:toUpperCase($str1)"/>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
For example, you can create this stylesheet as hello.xsl and apply it to any well-formed XML document. For example, run the oraxsl utility as follows:
oraxsl hello.xsl hello.xsl hello.out
The output document hello.out has the following content:
<?xml version = '1.0' encoding = 'UTF-8'?> HELLO WORLD
Using Return Value Extension Functions
The result of an extension function can be of any type, including the five types defined in XSL and the additional simple XML Schema data types defined in XSLT 2.0:
-
NodeSet -
Boolean -
String -
Number -
ResultTree
You can store these data types in variables or pass to other extension functions. If the result is of one of the five types defined in XSL, then the result can be returned as the result of an XSL expression.
The XSLT Processor supports overloading based on the number of parameters and type. The processor performs implicit type conversion between the five XSL types as defined in XSL. It performs type conversion implicitly among the following datatypes, and also from NodeSet to the following datatypes:
-
String -
Number -
Boolean -
ResultTree
Overloading based on two types that can be implicitly converted to each other is not permitted. The following overloading results in an error in XSL because String and Number can be implicitly converted to each other:
-
overloadme(int i){} -
overloadme(String s){}
Mapping between XSL datatypes and Java datatypes is done as follows:
String -> java.lang.String Number -> int, float, double Boolean -> boolean NodeSet -> NodeList ResultTree -> XMLDocumentFragment
The stylesheet in Example 6-6 parses the variable.xml document, which is located in the directory $ORACLE_HOME/xdk/demo/java/parser/xslt, and retrieves the value of the <title> child of the <chapter> element.
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0"
xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"
xmlns:parser = "http://www.oracle.com/XSL/Transform/java/oracle.xml.parser.v2.DOMParser"
xmlns:document =
"http://www.oracle.com/XSL/Transform/java/oracle.xml.parser.v2.XMLDocument">
<xsl:template match ="/">
<!-- Create a new instance of the parser and store it in myparser variable -->
<xsl:variable name="myparser" select="parser:new()"/>
<!-- Call an instance method of DOMParser. The first parameter is the object.
The PI is equivalent to $myparser.parse('file:/my_path/variable.xml'). Note
that you should replace my_path with the absolute path on your system. -->
<xsl:value-of select="parser:parse($myparser, 'file:/my_path/variable.xml')"/>
<!-- Get the document node of the XML Dom tree -->
<xsl:variable name="mydocument" select="parser:getDocument($myparser)"/>
<!-- Invoke getelementsbytagname on mydocument -->
<xsl:for-each select="document:getElementsByTagName($mydocument,'chapter')">
The value of the title element is: <xsl:value-of select="docinfo/title" />
</xsl:for-each>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
You can create Example 6-6 as gettitle.xsl and then run oraxsl as follows:
oraxsl gettitle.xsl gettitle.xsl variable.out
The output document variable.out has the following content:
<?xml version = '1.0' encoding = 'UTF-8'?> The value of the title element is: Section Tests
Tips and Techniques for Transforming XML
This section lists XSL and XSLT Processor for Java hints, and contains these topics:
Merging XML Documents with XSLT
"Merging Documents with appendChild()" discusses the DOM technique for merging documents. If the merging operation is simple, then you can also use an XSLT-based approach. Suppose that you want to merge the XML documents in Example 6-7 and Example 6-8.
<messages>
<msg>
<key>AAA</key>
<num>01001</num>
</msg>
<msg>
<key>BBB</key>
<num>01011</num>
</msg>
</messages>
<messages>
<msg>
<key>AAA</key>
<text>This is a Message</text>
</msg>
<msg>
<key>BBB</key>
<text>This is another Message</text>
</msg>
</messages>
Example 6-9 displays a sample stylesheet that merges the two XML documents based on matching the <key/> element values.
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output indent="yes"/>
<!-- store msg_w_text.xml in doc2 variable -->
<xsl:variable name="doc2" select="document('msg_w_text.xml')"/>
<!-- match each node in input xml document, that is, msg_w_num.xml -->
<xsl:template match="@*|node()">
<!-- copy the current node to the result tree -->
<xsl:copy>
<xsl:apply-templates select="@*|node()"/>
</xsl:copy>
</xsl:template>
<!-- match each <msg> element in msg_w_num.xml -->
<xsl:template match="msg">
<xsl:copy>
<xsl:apply-templates select="@*|node()"/>
<!-- insert two spaces so indentation is correct in output document -->
<xsl:text> </xsl:text>
<!-- copy <text> node from msg_w_text.xml into result tree -->
<text><xsl:value-of
select="$doc2/messages/msg[key=current()/key]/text"/>
</text>
</xsl:copy>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
Create the XML files in Example 6-7, Example 6-8, and Example 6-9 and run the following at the command line:
oraxsl msg_w_num.xml msgmerge.xsl msgmerge.xml
Example 6-10 shows the output document, which merges the data contained in msg_w_num.xml and msg_w_text.xml.
<?xml version = '1.0' encoding = 'UTF-8'?>
<messages>
<msg>
<key>AAA</key>
<num>01001</num>
<text>This is a Message</text>
</msg>
<msg>
<key>BBB</key>
<num>01011</num>
<text>This is another Message</text>
</msg>
</messages>
This technique is not as efficient for larger files as an equivalent database join of two tables, but it is useful if you have only XML files to work with.
Creating an HTML Input Form Based on the Columns in a Table
Suppose that you want to generate an HTML form for inputting data that uses column names from a database table. You can achieve this goal by using XSU to obtain an XML document based on the user_tab_columns table and XSLT to transform the XML into an HTML form.
-
Use XSU to generate an XML document based on the columns in the table. For example, suppose that the table is
hr.employees. You can run XSU from the command line as follows:java OracleXML getXML -user "hr/password"\ "SELECT column_name FROM user_tab_columns WHERE table_name = 'EMPLOYEES'" -
Save the XSU output as an XML file called
emp_columns.xml. The XML should look like the following, with one<ROW>element corresponding to each column in the table (some<ROW>elements have been removed to conserve space):<?xml version = '1.0'?><ROWSET> <ROW num="1"> <COLUMN_NAME>EMPLOYEE_ID</COLUMN_NAME> </ROW> <ROW num="2"> <COLUMN_NAME>FIRST_NAME</COLUMN_NAME> </ROW> <!-- rows 3 through 10 --> <ROW num="11"> <COLUMN_NAME>DEPARTMENT_ID</COLUMN_NAME> </ROW> </ROWSET> -
Create a stylesheet to transform the XML into HTML. For example, create the
columns.xslstylesheet as follows:<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform"> <xsl:output method="html"/> <xsl:template match="/"> <HTML> <xsl:apply-templates select="@*|node()"/> </HTML> </xsl:template> <xsl:template match="ROW"> <xsl:value-of select="COLUMN_NAME"/> <xsl:text> </xsl:text> <INPUT NAME="{COLUMN_NAME}"/> <BR/> </xsl:template> </xsl:stylesheet> -
Run the
oraxslutility to generate the HTML form. For example:oraxsl emp_columns.xml columns.xsl emp_form.htm
-
Review the output HTML form, which should have the following contents:
<HTML> EMPLOYEE_ID <INPUT NAME="EMPLOYEE_ID"><BR> FIRST_NAME <INPUT NAME="FIRST_NAME"><BR> LAST_NAME <INPUT NAME="LAST_NAME"><BR> EMAIL <INPUT NAME="EMAIL"><BR> PHONE_NUMBER <INPUT NAME="PHONE_NUMBER"><BR> HIRE_DATE <INPUT NAME="HIRE_DATE"><BR> JOB_ID <INPUT NAME="JOB_ID"><BR> SALARY <INPUT NAME="SALARY"><BR> COMMISSION_PCT <INPUT NAME="COMMISSION_PCT"><BR> MANAGER_ID <INPUT NAME="MANAGER_ID"><BR> DEPARTMENT_ID <INPUT NAME="DEPARTMENT_ID"><BR> </HTML>