RUN
Use the RUN command to group a series RMAN commands into a block to be executed sequentially. On reading the closing brace of the RUN block, RMAN compiles the list of job commands into one or more job steps and then executes the steps immediately.
Execute this command only at the RMAN prompt. You must precede the list of job commands with an opening brace ({) and terminate it with a closing brace (}).
You can use RUN to create a scope within which a script can override default configurations. For example, you can override configured channels with the ALLOCATE CHANNEL and RELEASE CHANNEL commands and other parameters with the SET command (as shown in Example 3-38). After executing the commands listed in the RUN block, the channels allocated within the RUN block are released and settings returned to their values.
As shown in Example 3-39, you must use the EXECUTE SCRIPT command within a RUN block.
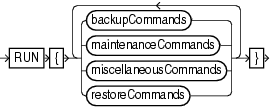
Description of the illustration run.gif
(backupCommands::=, maintenanceCommands::=, miscellaneousCommands::=, restoreCommands::=)
Description of the illustration backupcommands.gif
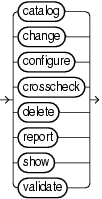
Description of the illustration maintenancecommands.gif
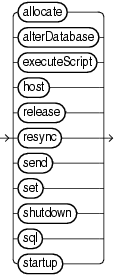
Description of the illustration miscellaneouscommands.gif
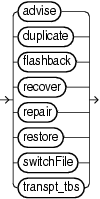
Description of the illustration restorecommands.gif
Refer to individual command entries for information about commands that you can run from the RMAN prompt.
Example 3-38 Overriding Configured Settings
Assume that your configured device configuration is as follows:
RMAN> SHOW DEVICE TYPE; RMAN configuration parameters for database with db_unique_name PROD1 are: CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE DISK PARALLELISM 1 BACKUP TYPE TO BACKUPSET; # default CONFIGURE DEVICE TYPE SBT_TAPE PARALLELISM 1 BACKUP TYPE TO BACKUPSET; # default
You want to make a backup to a nondefault directory. Instead of changing the configuration, you can override it in the job as follows:
RUN
{
ALLOCATE CHANNEL c1 DEVICE TYPE DISK FORMAT "/disk2/%U";
BACKUP DATABASE PLUS ARCHIVELOG;
}
Example 3-39 Executing an RMAN Script
Assume that you use the CREATE SCRIPT command to create a backup script named backup_db. This example executes the stored script:
RUN { EXECUTE SCRIPT backup_db; }