1 Introduction to XStream
This chapter introduces you to XStream, a new feature in Oracle Database 11g Release 2 (11.2). XStream enables information sharing with outstanding performance and usability.
This chapter contains the following topics:
About XStream
XStream consists of Oracle Database components and application programming interfaces (APIs) that enable client applications to receive data changes from an Oracle database and send data changes to an Oracle database. These data changes can be shared between Oracle databases and other systems. The other systems include non-Oracle databases, non-RDBMS Oracle products, file systems, third party software applications, and so on. A client application is designed by the user for specific purposes and use cases.
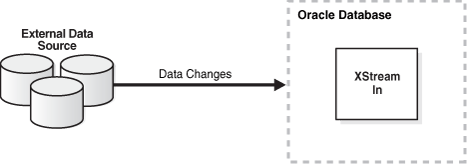
XStream consists of two major features: XStream Out and XStream In. XStream Out provides Oracle Database components and APIs that enable you to share data changes made to an Oracle database with other systems.
XStream In provides Oracle Database components and APIs that enable you to share data changes made to other systems with an Oracle database.
XStream is built on the infrastructure of Oracle Streams. Therefore, XStream inherits the flexibility and functionality of Oracle Streams, including:
-
The logical change record (LCR) format for streaming database changes
An LCR is a message with a specific format that describes a database change. If the change was a data manipulation language (DML) operation, then a row LCR encapsulates each row change resulting from the DML operation. One DML operation might result in multiple row changes, and so one DML operation might result in multiple row LCRs. If the change was a data definition language (DDL) operation, then a single DDL LCR encapsulates the DDL change.
-
Filtering of database changes at the database level, schema level, table level, and row/column level
-
Rules and rule sets that control behavior, including inclusion and exclusion rules
-
Rule-based transformations that modify captured data changes
-
Support for the data types supported by Oracle Streams, including LOBs,
LONG,LONGRAW, andXMLType -
Customized configurations, including multiple inbound streams to a single database instance, multiple outbound streams from a single database instance, multiple outbound streams from a single capture process, and so on
-
Full-featured apply for XStream In, including apply parallelism for optimal performance, SQL generation, conflict detection and resolution, error handling, and customized apply with apply handlers
Note:
In both XStream Out and XStream In configurations, the client application must use a dedicated server connection.Note:
When learning about and using XStream, a general knowledge of Oracle Streams concepts is helpful. See the following documents for conceptual information about Oracle Streams:-
Oracle Database 2 Day + Data Replication and Integration Guide contains basic conceptual information about Oracle Streams
-
Oracle Streams Concepts and Administration contains detailed conceptual information about Oracle Streams
Purpose of XStream
By using XStream, you can accomplish the following goals:
-
Replicate data changes
Replication is generally used to improve availability and to improve performance by spreading the network load over multiple regions and servers. XStream enables you replicate data changes made to an Oracle database with other Oracle databases and with non-Oracle data sources.
-
Store data changes in files
Some environments use files to store data changes for various reasons. For example, an environment might use files to store data changes if the environment does not have a physical network, if the environment uses disconnected computing, or if the environment uses satellite communications. After data changes are stored in files, the changes can be processed in any customized way by applications.
-
Share data changes with a client-side memory cache
Some environments share data changes with a client-side memory cache to improve performance.
See Also:
Chapter 3, "XStream Use Cases"Prerequisites for XStream
Using the XStream APIs requires purchasing a license for the Oracle GoldenGate product. See the documentation for the Oracle GoldenGate product for more information:
http://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E15881_01/index.htm
In addition, this document assumes that you have the following skills:
-
Knowledge of relational database concepts and Oracle Database concepts
XStream includes components that run in an Oracle database. To use XStream successfully, you must be able to administer an Oracle Database.
See Oracle Database Concepts for information about this topic.
-
Knowledge of distributed databases
An XStream environment includes multiple data sources, including Oracle databases and non-Oracle data sources. You should understand distributed database concepts before using XStream.
See Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information about this topic.
-
Knowledge of SQL and PL/SQL
To administer an Oracle database and the XStream components running in an Oracle database, you must know how to use SQL and PL/SQL.
See Oracle Database SQL Language Reference, Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference, and Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information about this topic.
-
Knowledge of application programming
XStream Out sends data changes to a client application for processing. XStream In receives data changes from a client application. You use the Oracle Call Interface (OCI) API or the Java API to create a client application that communicates with XStream.
See Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide for information about the OCI API.
See Oracle Database 2 Day + Java Developer's Guide and Oracle Database Java Developer's Guide for information about the Java API.
Tasks and Tools for XStream
This section describes the common tasks you perform for XStream and the tools to use to complete the tasks.
This section contains the following topics:
XStream Tasks
The common tasks for XStream are the following:
-
Configure XStream
Configuring XStream involves preparing an Oracle Database for XStream, creating the Oracle Database components used by XStream, and creating one or more client applications that communicate with the Oracle Database.
See Chapter 4, "Configuring XStream" for information about this task.
-
Administer XStream
Administering XStream involves managing the Oracle Database components used by XStream. It also involves managing the rules and rule sets used by these components. It might also require modifications to a client application.
See Chapter 5, "Managing XStream" for information about this task.
-
Monitor XStream
Monitoring XStream involves viewing Oracle Enterprise Manager pages related to XStream and querying data dictionary views related to XStream.
See the Oracle Enterprise Manager online help and Chapter 6, "Monitoring XStream" for information about this task.
XStream Tools
Use the following tools to complete the tasks for XStream:
-
SQL and PL/SQL
You can use SQL and PL/SQL to configure, administer, and monitor XStream. SQL enables you to create an XStream administrator and monitor XStream using data dictionary views. Several Oracle-supplied PL/SQL packages enable you to configure and manage XStream.
See Oracle Database SQL Language Reference, Oracle Database PL/SQL Language Reference, and Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information about this topic.
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager
You can use Enterprise Manager to manage and monitor XStream components. You can also use Enterprise Manager to view information about the LCRs that are streaming in an XStream configuration.
See the Enterprise Manager online help for more information about this topic.
-
The OCI API and Java API
You can use the XStream OCI API and XStream Java API to create client application that communicate with XStream. These applications can work with XStream Out to stream LCRs out of an Oracle Database, and these applications can work with XStream In to stream LCRs into an Oracle Database.
See Part IV, "XStream OCI API Reference" for information about the XStream OCI API, and see Oracle Call Interface Programmer's Guide for information about the OCI API.
See Oracle Database XStream Java API Reference for information about the XStream Java API, and see Oracle Database 2 Day + Java Developer's Guide and Oracle Database Java Developer's Guide for information about the Java API.