3 Building a Simple .NET Application Using ODP.NET
This chapter contains:
Creating a New Project
Visual Studio groups all development code that you create into containers known as projects. Simpler projects often contain only one file. In this section, you will learn how to create a new development project.
The application you build in this chapter serves as a starting point for work in subsequent chapters, so it is important to follow the order of this guide.
NOTE: When necessary, instructions specify Visual C# or Visual Basic.
-
Start Visual Studio.
Open the Start menu, select All Programs, and then select Microsoft Visual Studio 2008.
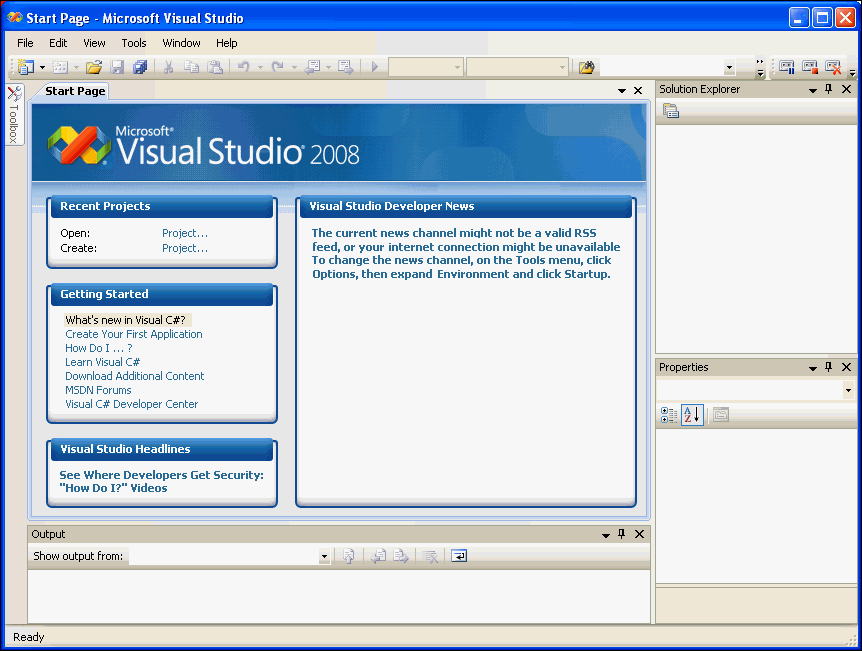
Description of the illustration connect00.gif
The Microsoft Visual Studio IDE environment appears.
-
In the Start Page, under the Recent Projects heading, click Create: Project.
Alternatively, from the File menu, select New, and then select Project.
A New Project dialog box appears.
-
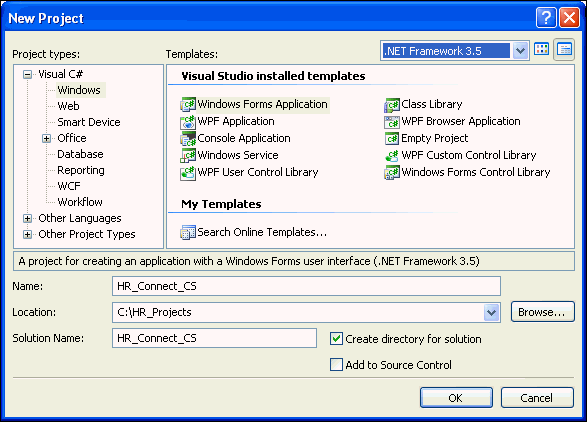
In Project Types, select the type of project you are creating:
Visual C#:
Visual C#: Windows
Visual Basic:
Other Languages: Visual Basic: Windows
-
In Templates, select Windows Forms Application.
-
In the Name field, enter the appropriate name.
Visual C#:
HR_Connect_CS
Visual Basic:
HR_Connect_VB
The abbreviation
CSindicates C# projects and VB indicates Visual Basic projects. -
In Location, enter the directory where you want to save the files.
For this guide, enter this directory
C:\HR_Projects. -
In Solution Name, the appropriate name, HR_Connect_CS or HR_Connect_VB should appear.
A solution can contain several projects; when it contains only one project, you can use the same name for both.
-
Check Create directory for solution.
-
Click OK.
-
Description of the illustration connect01.gif
The project is created.
The main window now displays a new title, either HR_Connect_CS - Microsoft Visual Studio or HR_Connect_CS - Microsoft Visual Studio, depending on the language, and contains Form1 shown below.
It is important to remember that many projects automatically name the first form Form1. This is the name of the form control. Do not confuse this with the actual name given to the code file, which is typically
Form1.csorForm1.vb.Both Form1 and
Form1.xxcan be renamed. For the purposes of this guide, we will renameForm1.xxseveral times.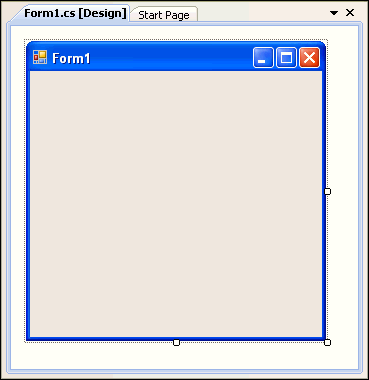
Description of the illustration connect2a.gif
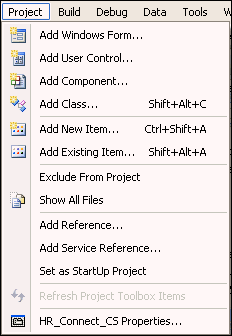
Adding a Reference
This section shows you how to add a reference to the Oracle.DataAccess.dll file, which contains the data provider, Oracle Data Provider for .NET.
-
From the Project menu, select Add Reference.
Description of the illustration reference01.gif
The Add Reference windows appears.
-
In the Add Reference window, under the .NET tab, select Oracle.DataAccess. Click OK.
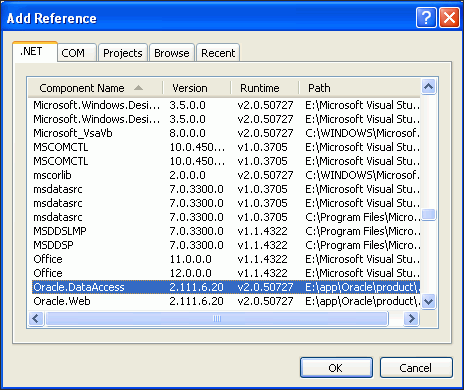
Description of the illustration reference02.gif
Note that the new reference appears in the Solution Explorer.
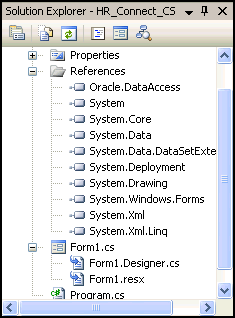
Description of the illustration reference03.gif
Adding Namespace Directives
You can add Oracle namespace directives that allow you to indicate an assembly's namespaces within the module. To do this, add C# using statements or Visual Basic Imports statements, at or near the top of a code file.
Note:
Adding a reference makes the namespace available within the application. Adding a namespace directive within the application code makes the namespace more visible and allows for additional scoping.To add Oracle namespace directives:
-
With Form1 active, from the View menu select Code.
Alternatively, you can use the F7 keyboard shortcut.
Description of the illustration connect04.gif
-
Add the following statements to the list of declarations depending on the language you are using.
-
Visual C#:
Add with other
usingstatements, before the namespace.using Oracle.DataAccess.Client; using Oracle.DataAccess.Types;
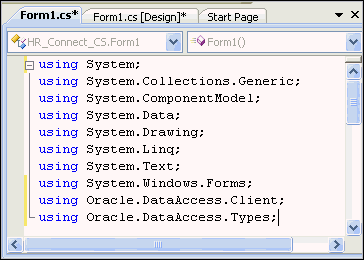
Description of the illustration connect05.gif
-
Visual Basic:.
Add to the top of the file, in the declarations section.
Imports Oracle.DataAccess.Client Imports Oracle.DataAccess.Types
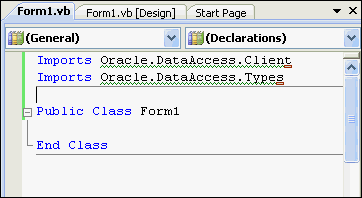
Description of the illustration connect06.gif
-
-
Save the changes by selecting Save from the File menu, or using the Ctrl+S keyboard shortcut.
Designing the User Interface
You can create a user interface by adding the toolbox controls to the design form. This interface accepts connection information from the user.
-
From the View menu, select Designer.
This opens Form1, in design view, if it is not already open.
You will toggle between Code and Designer a lot. The keyboard shortcuts are F7 and shift- F7 respectively.
-
From the View menu, select Toolbox.
-
In the Toolbox, expand Common Controls.
Description of the illustration control01.gif
-
In the Toolbox, select Label, and drag it onto the Form1.
Description of the illustration control02.gif
-
On Form1, right-click label1.
Description of the illustration control03.gif
-
From the menu, select Properties, if the Properties Window is not already visible.
The Properties Window appears.
-
In the Properties Window, change the Text property from label1 to User ID.
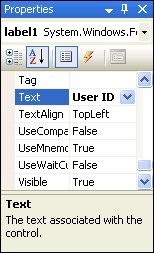
Description of the illustration control04.gif
-
Repeat steps 4 through 7 twice, placing two more labels on Form 1 and changing their text properties to Password and Data Source.
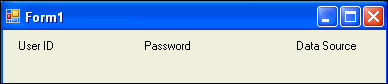
Description of the illustration control05.gif
-
In the Toolbox, select TextBox, and drag it onto the Form1, next to the User ID label.
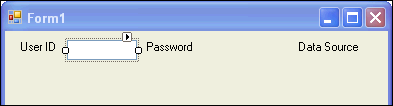
Description of the illustration control06.gif
-
In the Properties Window, change the Name property to userID.
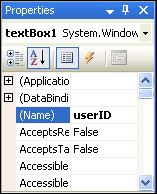
Description of the illustration control07.gif
-
Repeat steps 9 and 10 twice, positioning two more text boxes next to the existing labels, and setting the Name property to password and dataSource.
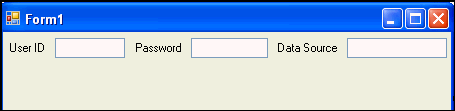
Description of the illustration control08.gif
-
Select the text box next to the Password label. In the Properties Window, scroll to the PasswordChar property and set it to an asterisk (*).
This masks the password during entry.
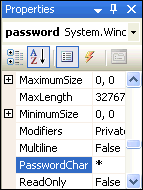
Description of the illustration control09.gif
-
From the Toolbox, select Button and drag it onto Form1.
In the Properties Window, change the Text property of the button from button1 to Connect, and change the Name property to connect.
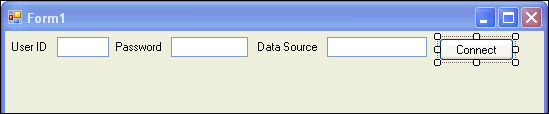
Description of the illustration control10.gif
-
Save.
-
Close the Toolbox.
Writing the Connection Code
Now we write the code that takes the information provided to the user interface and connects to the database.
To connect to the database, you must create a connection object.
To write code that connects to the database:
These steps enable your application to connect to the database based on data that the user enters into the Form1 control. See "Compiling and Running the Application".
-
From the View menu, select Code.
-
Add the code indicated to instantiate a database connection string.
Visual C#: Add the class variable
connto theForm1class right after thepublicForm1()block with this code.private OracleConnection conn = new OracleConnection();
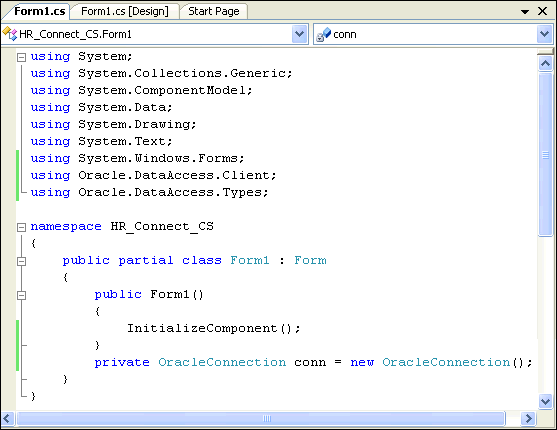
Description of the illustration connect1.gif
Visual Basic: Add the
connclass variable in theForm1class declaration, using this code.Public Class Form1 Dim conn As New OracleConnection
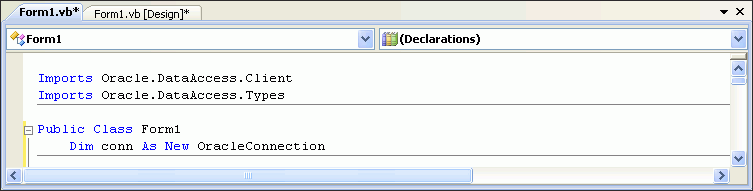
Description of the illustration connect2.gif
-
Save your changes.
-
Change to Designer view by clicking on the View menu and selecting Designer.
-
Double-click the Connect button on Form1 to open the code window to the
connect_Click()method.Insert the code indicated into the
connect_Click()method.Visual C#:
conn.ConnectionString = "User Id=" + userID.Text + ";Password=" + password.Text + ";Data Source=" + dataSource.Text + ";"; conn.Open();
Visual Basic:
conn.ConnectionString = "User Id=" + userID.Text & _ ";Password=" + password.Text & _ ";Data Source=" + dataSource.Text conn.Open()
Note: Before a connection can be opened, it must be built from user input for the
UserID,Password, andDataSource. TheOpen()method makes the actual connection. -
Set the
Enabledattribute of the button tofalseby inserting the indicated code at the end of theconnect_Click()method.This disables the
Connectbutton, which is a good practice once a connection is successfully made.Visual C#:
connect.Enabled = false;
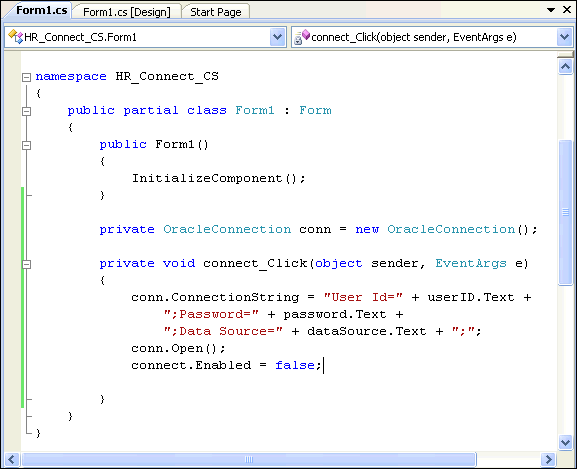
Description of the illustration connect_obj1.gif
Visual Basic:
connect.Enabled = false
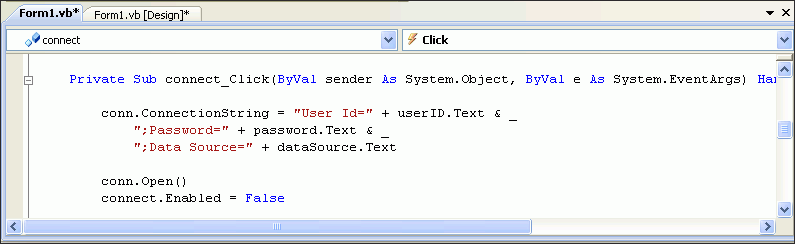
Description of the illustration connect_obj2.gif
You have now finished writing an application that can connect to the Oracle database. The following sections show how to use it.
Compiling and Running the Application
This section shows how to compile and run the application you created in the previous sections.
To compile and run the application:
-
From the Build menu, select Build Solution.
Description of the illustration build1.gif
-
Ensure that there are no errors reported in the output window, available from the View menu.
The following graphics shows a typical output result.
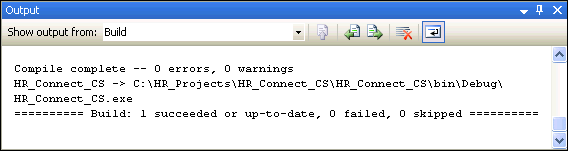
Description of the illustration build2.gif
-
If there are any errors indicated, from the View menu, select Error List and fix the errors.
-
From the Debug menu, select Start Without Debugging to run the application.
Description of the illustration build3.gif
-
In the Form1 application, enter the User ID, Password, and Data Source.
Click Connect.
This is where the application makes use of the
tnsnames.orafile. See "Configuring a NET Connect Alias".Once the connection is opened, the Connect button is disabled. You have succeeded in implementing a connection to an Oracle Database instance.
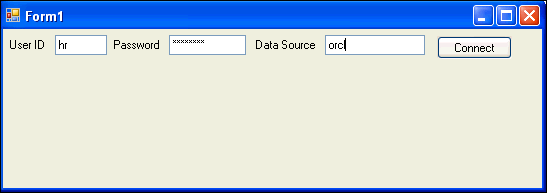
Description of the illustration build4.gif
Error Handling
Applications must be able to handle run-time errors gracefully. For example, if you try to log in using an incorrect password, the application you developed so far cannot establish a connection to the database, and exits with the following unhandled exception error, ORA-1017: invalid username/password, logon denied.
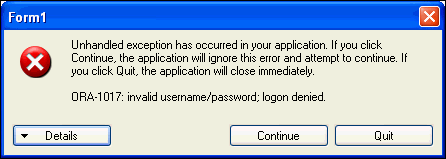
Description of the illustration error1.gif
You must reselect Start Without Debugging to try this with a different password.
Error handling manages occurrences of conditions that change the normal flow of program execution. Oracle Data Provider for .NET contains three classes for error handling and support:
-
The
OracleErrorclass represents a warning or an error reported by Oracle. -
An
OracleErrorCollectionclass represents a collection of all errors that are thrown by the Oracle Data Provider for .NET. It is a simpleArrayListthat holds a list ofOracleErrors. -
The
OracleExceptionclass represents an exception that is thrown when the Oracle Data Provider for .NET encounters an error. EachOracleExceptionobject contains at least oneOracleErrorobject in theErrorproperty that describes the error or warning.
Using Try-Catch-Finally Block Structure
.NET languages use Try-Catch-Finally block structure for error handling. With this structure, the Try code is the main code, the goal that the application wants to accomplish. The Catch code catches errors of various types, as shown in the next two section. The Finally block comes last and always executes.
The Finally block frequently contains the Dispose method, which closes and disposes of the connection. Having the Dispose method in the Finally block ensures that the database connection is always closed after the Try-Catch-Finally block completes. Closing database connections after the application no longer requires database access is important for many reasons, especially data security.
Attempting to close a closed database connection does not cause an error. The attempt is irrelevant. Nonetheless, placing Dispose() in the Finally code block guarantees that the connection is closed.
The next section shows how to use Try-Catch-Finally block structure with general errors, and the section after that, with Oracle errors.
Handling General Errors
This section shows how to handle general errors using a Try-Catch-Finally block.
-
Change the code of the
connect_Click()method inForm1by adding an implementation of the Try-Catch-Finally syntax.New code is in bold font.
Visual C#:
private void connect_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { conn.ConnectionString = "Data Source=ORCL;User Id=" + userID.Text + ";Password=" + password.Text + ";"; try { conn.Open(); connect.Enabled = false; } catch (Exception ex) { MessageBox.Show(ex.Message.ToString()); } finally { conn.Dispose(); } }Alternatively, you can use C# syntax that disposes of a connection when it goes out of scope, with the
usingkeyword, as follows:using (OracleConnection conn = new OracleConnection()) { conn.Open(); // application code ... }
Visual Basic:
Try conn.Open() connect.Enabled = false Catch ex As Exception MessageBox.Show(ex.Message.ToString()) Finally conn.Dispose() End Try
-
From the Build menu, select Rebuild Solution.
Ensure that there are no errors.
-
From the Debug menu, select Start Without Debugging.
-
Run the application again, as described in section "Compiling and Running the Application", and attempt to connect using an incorrect password. This time, the application catches the error and displays it in a pop-up window,
ORA-1017: invalidusername/password;logondenied.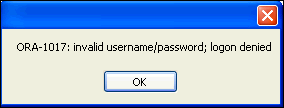
Description of the illustration error2.gif
Handling Common Oracle Errors
In the completed Try-Catch-Finally block code shown below, the first Catch statement branch is skipped if there are no OracleExceptions. The second Catch statement branch catches all other Exceptions.
The first catch statement contains Case statements, which can be used to trap common database errors and display them in a user-friendly manner.
Note that the second Case statement catches a specific example of OracleException, when the database is not accessible.
-
Stop the database instance. See Appendix A, "Starting and Stopping an Oracle Database Instance".
-
Add the
CatchOracleExceptionblock shown below in bold, before theCatchExceptionblock previously added in theconnect_Click()method.Visual C#:
try { conn.Open(); connect.Enabled = false; } catch (OracleException ex) { switch (ex.Number) { case 1: MessageBox.Show("Error attempting to insert duplicate data."); break; case 12560: MessageBox.Show("The database is unavailable."); break; default: MessageBox.Show("Database error: " + ex.Message.ToString()); break; } } catch (Exception ex) { MessageBox.Show(ex.Message.ToString()); } finally { conn.Dispose(); } }
Visual Basic:
Try conn.Open() connect.Enabled = false Catch ex As OracleException ' catches only Oracle errors Select Case ex.Number Case 1 MessageBox.Show("Error attempting to insert duplicate data.") Case 12560 MessageBox.Show("The database is unavailable.") Case Else MessageBox.Show("Database error: " + ex.Message.ToString()) End Select Catch ex As Exception MessageBox.Show(ex.Message.ToString()) Finally conn.Dispose() End Try
-
Compile and run the application again, as described in section "Compiling and Running the Application".
Note that the
ORA-12560error appears in the pop-up window asThedatabaseisunavailablewith no error number provided.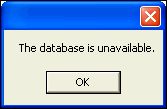
Description of the illustration error04.gif
-
Restart the database instance. See Appendix A, "Starting and Stopping an Oracle Database Instance".